To ensure the normal differentiation of strawberry flower buds, use Monband® program
Flower bud differentiation of strawberry is an important process in strawberry planting. Once the flower bud differentiation is not good, it will greatly affect the planting and management of strawberries.Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to flower bud differentiation of strawberry, and understand the process and influencing factors of flower bud differentiation before planting.

First, the process of flower bud differentiation.
The flower bud differentiation of strawberry can be divided into two stages: physiological differentiation and morphological differentiation. The physiological differentiation stage is mainly the change of internal growth point. It is a process of gradual accumulation of nutrients, hormones and genetic material to form flowers. This stage is difficult to observe and is usually completed when the strawberries are growing.
When the accumulation of flower-forming substances in the growing point reaches a certain threshold, the growth point begins to undergo morphological changes, and it enters the stage of morphological differentiation. This stage can be observed through a microscope.
The process of morphological differentiation can be divided into three stages: initial differentiation stage, inflorescence differentiation stage and flower organ differentiation stage. Among them, in the early stage of differentiation, the growth point begins to become hypertrophy and bulge, and gradually forms the original body of the top flower, which takes about 5-6 days. After the growth point thickened, the longitudinal split appeared, marking the formation of the primordium of the top flower, and then entered the stage of inflorescence differentiation.
At this stage, the flower bud group of the top inflorescence continues to develop until the sepals begin to bulge and develop, which takes about 11 days. Entering the floral organ formation stage, each organ of the flower develops formally from the outside to the inside according to the sequence of sepals, petals, stamens, pistil, etc. The final retraction of the sepals marks the formation of the apical inflorescence.
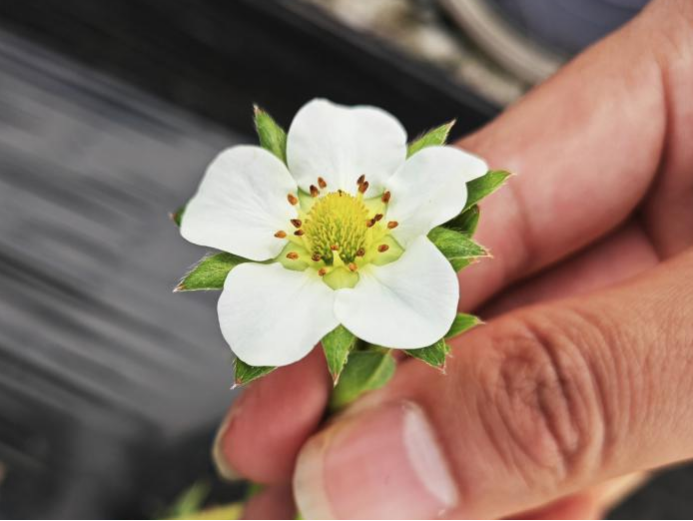

Second, the influence factors of flower bud differentiation.
1. Temperature and light
Strawberry flower bud differentiation needs low temperature and short sunshine environment. At 5-10℃, strawberry flower buds can differentiate regardless of the length of sunshine, but the flowers that grow slowly will be weaker. At 10-25℃, the differentiation of flower buds was affected by the length of sunshine, and the shorter the length of sunshine, the more favorable the differentiation of flower buds. When the temperature is above 25℃, no matter the length of sunshine time, the flower bud can not differentiate.
Based on this situation, it is possible to create a short-day environment of geothermal temperature by postponing the mulch film, the shed film, and the sunshade net. In addition, calcium can improve the ability of strawberries to respond to low temperature and short sunshine, so calcium fertilizer needs to be added in the early stage.
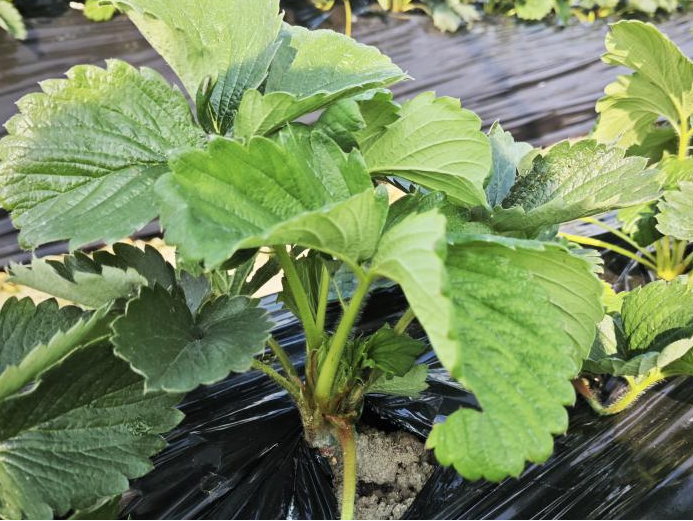

2. Old leaves
It was found that the removal of strawberry old leaves could effectively promote the differentiation of strawberry flower buds. In the extreme experiment, when all strawberry leaves were removed, flower bud differentiation could be carried out under 16 hours of long day.
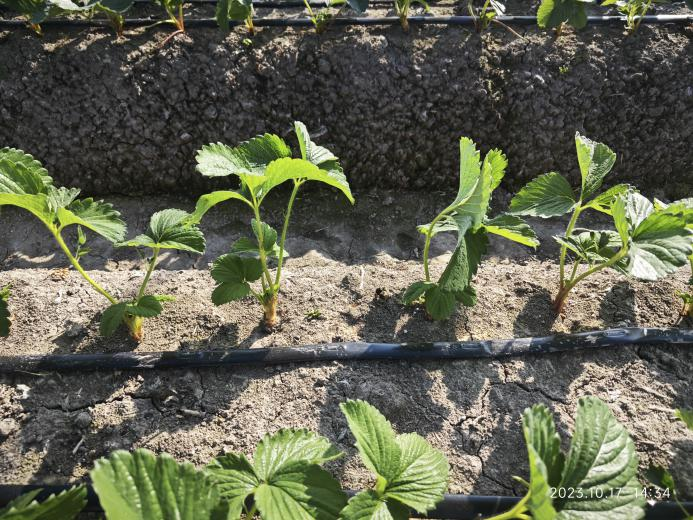

3. Control growth
Research has found that before flower buds differentiate. Soluble sugar, reducing sugar, starch and other substances accumulate in the leaves to supply the consumption of nutrients during flower bud differentiation.
These substances can not only provide energy for flower bud differentiation, but also provide carbon scaffolding for protein synthesis. Therefore, in order to promote flower bud differentiation, it is necessary to control the nutritional growth of strawberries and store these nutrients.
The accumulation of starch in the leaves will make the leaves darker, so we can judge the degree of nutrient accumulation by whether the leaf color is thick green. Also pay attention to the nitrogen content of strawberries. If it is too high, it will inhibit the ability of strawberry to sense short sunshine and is not conducive to flower bud differentiation.
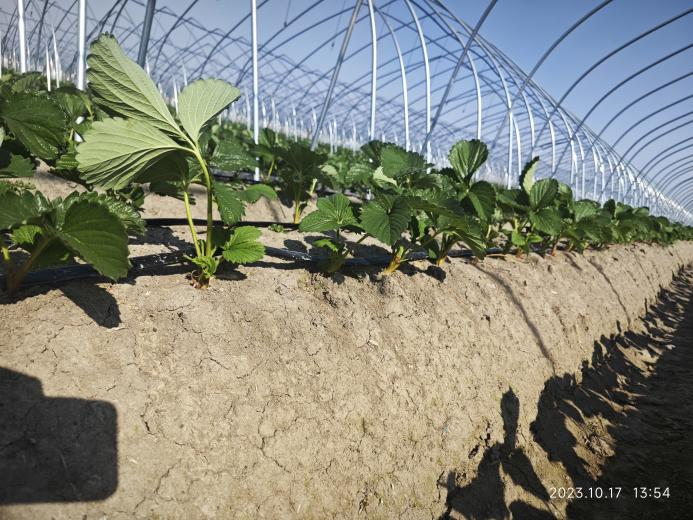

In the later period, the excessive use of drugs to control the growth of flowers is not conducive to the extraction of flower branches. Nutrition control should be chosen at this time. It is possible to choose the Monband® nutrition program to effectively shift vegetative growth to reproductive growth, thus promoting flower bud differentiation.




 Learn more
Learn more
 冀公网安备13019902000986
冀公网安备13019902000986